BASIC GRAMMAR CONCEPTS (PHONOLOGY, MORPHOLOGY, AND SYNTAX)
- Project director: MA. in ELT. Cesar Jaimes Jaimes / Sandra Albiter Jaimes; Aislinn Pérez Jaramillo

- 20 feb 2021
- 5 Min. de lectura
Actualizado: 9 abr 2021
Grammar is the part of Linguistics that studies the set of rules and principles that govern a language. Grammar comes from the Latin grammatĭca, and this in turn from the Greek γραμματική (grammatiqué), which derives from γράμμα (gramma), which means ‘letter’, ‘written’.
"The study of what forms (or structures) are possible in a language" Thornbury 1999:1
Phonology
Is the branch of linguistics that studies the sound system of the language in general, and of each language in particular, including syllables, intonation, stress, at an abstract or mental level.
The study of the structure and systematic patters of sounds in human language.

CLASSIFICATION:
Diachronic phonology
synchronic phonology
generative phonology
phonology and phonetics
minimal pairs
allophones
phonemes
syllable structure
phonotactics
Phonemes:
Distinctive or contrastive sound (phonological segment) in the sound system of a language.

Phonotactics:
Study of the sound and phoneme combinations allowed in a given language.

Phonotactics Constraints:
The rules that characteristic permissible syllable structures in a language.

Phonemics:
narrow study of sounds. Example: [Ph] in peak, [p] in speak.

Phonetics:
Broad study of sounds. This section of linguistics studies the sounds of human language and is divided into:
1) Articulatory phonetics
2) Acoustic phonetics
3) auditory phonetics

Monophthong: a vowel to which only one sound is perceived. unlike diphthongs, a "monophthong" does not "slide" up or down in relation to another vowel. for Example: eh/ in the word "pet", in / in the word "film" and aa/ in the word "father".

Diphthong:
Asound that is formed by combining two vowels into a single syllable in wich the sound begins at one vowel and moves to the other, for example: ey/ in the word "play", oy/ in the word "boy" and aw/ in "loud".

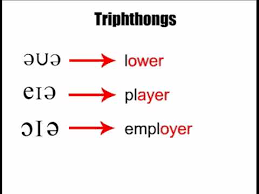
Triphthong: union of three vowels (letters or sounds) that are pronounced in a single syllable. they are pronounced together as if the sound were passing smoothly from one letter to another.
Allophonic: Aspiration in English is an example of a predictable allophonic. Occurs with certain consonants at the beginning of a word (if the syllable is stressed).

What is Phonological Knowledge?
We all have instructional knowledge of the phonemes of our own language.
It allows us to produce sounds that form meaningful utterances (even if they are new)
It allows us to recognize and understand a foreign accent.

Morphology
Is the branch of linguistics that studies the internal structure of words to define and classify their units: the variants of words and the formation of new words.
It is worth mentioning that morphology comprises the part of grammar that deals with classifying and explaining the funtioning and meaning of variations in the form of words within the structure of the language.

Two basic goals in studying morphology:
To isole the component parts of words
to determine the rules by which words are formed
Classification:
Inflectional morphology: It is study of the processes (such as affixation) that distinguish the forms of words in certain grammatical categories.
Derivative morphology: Deals with the processes of formation of new lexemes or words.
Morpheme: Is the minium unit of the language that has lexical or grammatical meaning.
Lexical category: Are those words with referential and semantic content, unlike functional categories that have mainly grammatical content.
Grammatical category: Are the 9 types of words that there is noun, pronoun, determiner, adjective, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
Affixes: Is called the linguistic sequence that modifies the meaning of a concept.
Prefixes: An affix that is placed before the term to be modified.
Suffixes: It is placed at the end of the term.
Infixes: It is inserted in the middle of the word.
Circumfix: Is a type of discontinuous affix, that is, an affix consisting of the intention of two separate parts in a word.

Morphology fulfills three specific functions: It categorizes words according to their function, studies the variations in their forms and explains the processes involved in the derivation and composition of words.

Morpheme:
It is a part of a word that changes meanings, makes one part of speech into another, and shows such grammatical functions as tense and plurality.
Example: buyers [buy] + [er] + [s]

Bound and Free Morphemes
Bound Morphemes- cannot occur unattached.
Free Morphemes- can stand on its own. (root words and function words).
Example: glasses glass- free morpheme is- bound morpheme
Syntax

Syntax is the ways that words can be put together, or are put together, in order to make sentences.
The term "syntax" comes from the Greek, meaning "arrange together".
The part of linguistics that studies sentences structure:
- Word order
-Agreement
-How many complements, which prepositions and forms (classes)
-Hierarchical structure.

Words do not operate individually and in isolation, but in a chain or string, some before others, since their own meaning can be altered from their place in the sentence. in fact, the spanish syntax establishes a default order in wich the sentences are formuled, which we know as SVP.
Subject: it is how the noun phrase is called, that is, the set of words that fulfill the role within the sentence of indicating on whom the action of the verb falls.

Verb: it is the word that indicates the action in the sentence, and therefore it is always in agreement with the nucleus of the subject.

Predicate: it is how we call the verb phrase, that is, everything that is neither subject, its core always being the verb itself.
Classification:
*Normal or regular syntax
*irregular syntax

The syntactic Categories
-Noun: They refer to people, places or things. even intangible or abstract concepts like ideas or thoughts are things.

-Pronoun: Are words that replace nouns- I, me, she, we, they, who, that, etc.

-Verb: Are action words. Verbs tell you what the subject of the sentences is up to.

-Adjectives: Are descriptive words that add detail to a sentence.

-Adverb: It is a word that modifities (describes) a verb, and adjective, another adverb, or even whole sentence.

-Prepositions: Are a little words that tell where or when (among other things) and round.

-Conjunctions: Are words like and, but and or that connect concepts, classes or parts of sentences.
-Articles: Modify nouns. English has two articles the and a/an.


What is the Syntax for?
The syntax is of central importance in grammar since it teaches us the possible orders of language, that is, it indicates the allowed and not allowed combinations of words to obtain recognizable meanings.
A good command of the syntax not only allows us to distinguish acceptable from unacceptable formulations, but at the same time to vary the way in which we construct our sentences, thus being able to take better advantage of the limits of the language in terms of creativity, eloquence, poetry, etc.
AUDIOLINGUAL- METHOD
The method that we use for develop the model class was the Audiolingua-method. this method consist on dialogues and repetition exercises are the basis in the classroom. dialogues provide context to language and are used for repetition and memorization.
The method objetive is training in oral comprehension, phonetic correction, recognition of speech symbols as graphic signs, and the ability to produce those symbols in writing.
The strategies used in this method are: Repetition, dialogue, memorization, substitution and reformulation.

Bibliography
Catillo, I. (19 de febrero de 2021). lifeder. Recuperado el 12 de febrero de 2021, de lifeder: http://www.lifeder.com/morfologia-linguistica/
Mateos, C. (26 de Enero de 2018). Medium. Recuperado el 13 de febrero de 2021, de https://medium.com/@mateoskarla93/morfolog%C3%ADa-959e3c929c85
Raffino, M. E. (17 de septiembre de 2020). Concepto d. Recuperado el 12 de febrero de 2021, de https://concepto.de/fonetica/
Arturo. (15 de enero de 2021). Ejemplo de.com. Recuperado el 14 de febrero de 2021, de https://www.ejemplode.com/12-clases_de_espanol/3236-ejemplo_de_sintaxis.html




Comentarios